xfit_premelt
Master curve maxwell scaling using near-solidus parametrization of Yamauchi and Takei (2016), J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth, DOI with optional extension to include direct melt effects of Yamauchi and Takei (2024), J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth, DOI.
Requires
The following state variable arrays are required:
VBR.in.SV.Tsolidus_K % solidus temperature [K]
VBR.in.SV.T_K % temperature [K]
VBR.in.SV.P_GPa % pressure [GPa]
VBR.in.SV.dg_um % grain size [um]
VBR.in.SV.sig_MPa % differential stress [MPa]
VBR.in.SV.phi % melt fraction / porosity
VBR.in.SV.rho % density in kg m<sup>-3</sup>
To use the Yamauchi and Takei (2024) scaling that includes direct melt effects, set the following flag:
VBR.in.anelastic.xfit_premelt.include_direct_melt_effect = 1;
Additionally, xfit_premelt relies on output from the elastic and viscous methods.
Required Elastic Methods: anharmonic MUST be in the VBR.in.elastic.methods_list. Poroelasticity
is treated differently depending on the value of include_direct_melt_effect.
If include_direct_melt_effect==0 and anh_poro is in the methods list then xfit_premelt will use the unrelaxed moduli
from anh_poro (which includes the P,T projection of anharmonic plus the poroelastic correction). See the section
on elastic methods for more details. If include_direct_melt_effect==1, then poroelasticity is incororated within
J1, following Yamauchi and Takei (2024). The current version of the VBRc uses include_direct_melt_effect=0 as the default,
future versions will set this flag to 1 by default.
Optional Viscous Methods: xfit_premelt calculates maxwell times using the viscous xfit_premelt method.
If you want to adjust the viscosity calculation used in the maxwell time, you can add xfit_premelt to VBR.in.viscous.methods_list
and adjust the desired parameters. The anelastic calculation will then use the results calculated by the viscous xfit_premelt method.
This is particularly useful when fitting laboratory measurements of borneol (see example below).
Calling Procedure
% set required state variables
clear
VBR.in.SV.T_K=700:50:1300;
VBR.in.SV.T_K=VBR.in.SV.T_K+273;
sz=size(VBR.in.SV.T_K); % temperature [K]
% remaining state variables (ISV)
VBR.in.SV.dg_um=3.1*ones(sz);
VBR.in.SV.Tsolidus_K=(1200+273)*ones(sz);
VBR.in.SV.P_GPa = 0.2 * ones(sz); % pressure [GPa]
VBR.in.SV.rho = 3300 * ones(sz); % density [kg m^-3]
VBR.in.SV.sig_MPa = 10 * ones(sz); % differential stress [MPa]
VBR.in.SV.phi = 0.0 * ones(sz); % melt fraction
% set frequency range
VBR.in.SV.f = 1./logspace(-2,4,100);
% set elastic methods list (at least 'anharmonic' is required)
VBR.in.elastic.methods_list={'anharmonic';'anh_poro'};
% set anelastic methods list
VBR.in.anelastic.methods_list={'xfit_premelt'};
% enable melt effects from Yamauchi and Takei (2024)
VBR.in.anelastic.xfit_premelt.include_direct_melt_effect = 1;
% call VBR_spine
[VBR] = VBR_spine(VBR) ;
Output
Output is stored in VBR.out.anelastic.xfit_premelt:
>> disp(fieldnames(VBR.out.anelastic.xfit_premelt))
{
[1,1] = J1 % real part of dynamic compliance [1/Pa]
[2,1] = J2 % complex part of dynamic compliance [1/Pa]
[3,1] = V % shear wave velocity [m/s]
[4,1] = M1 % 1/J1 [Pa]
[5,1] = M2 % 1/J2 [Pa]
[6,1] = Qinv % attenuation
[7,1] = Q % quality factor
[8,1] = M % modulus [Pa]
[9,1] = Vave % frequency-averaged shear wave velocity [m/s]
}
The following fields are frequency dependent: J1,J2,Q,Qinv,M1,M2,M, V.
Parameters
To view the full list of parameters,
VBR.in.anelastic.xfit_premelt = Params_Anelastic('xfit_premelt');
disp(VBR.in.anelastic.xfit_premelt)
Any of the parameters can be set before calling VBR_spine.
Example at Laboratory Conditions
The Project script, Projects/1_LabData/1_Attenuation/FitData_YT16.m calculates attenuation and modulus for borneol sample 41 at temperatures of 8, 13, 18, 29, 35, 39 and 47oC following Yamauchi and Takei (2016):
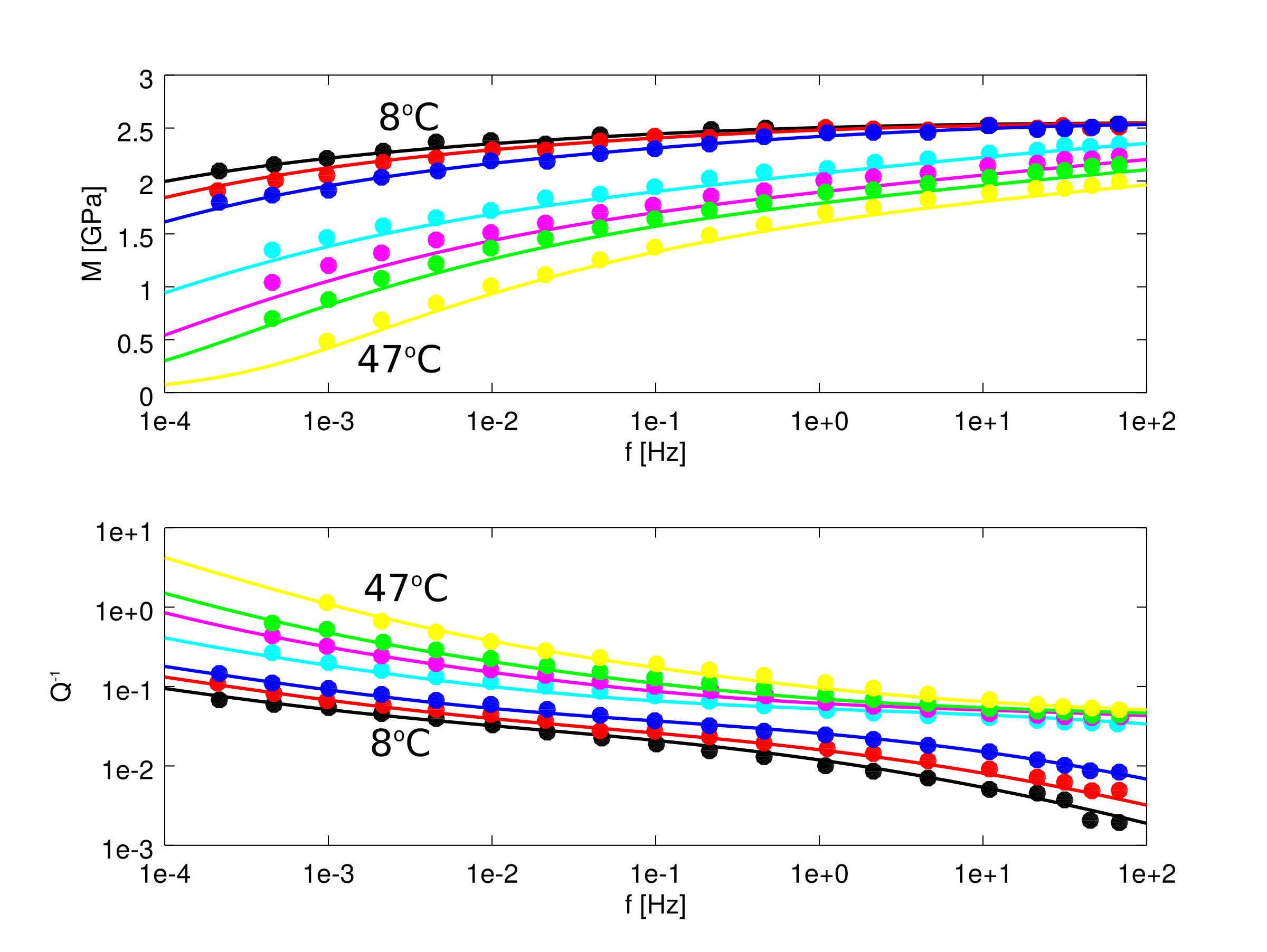
Data are from figure 10 of Yamauchi and Takei (2016) and are not included in the repository at present.
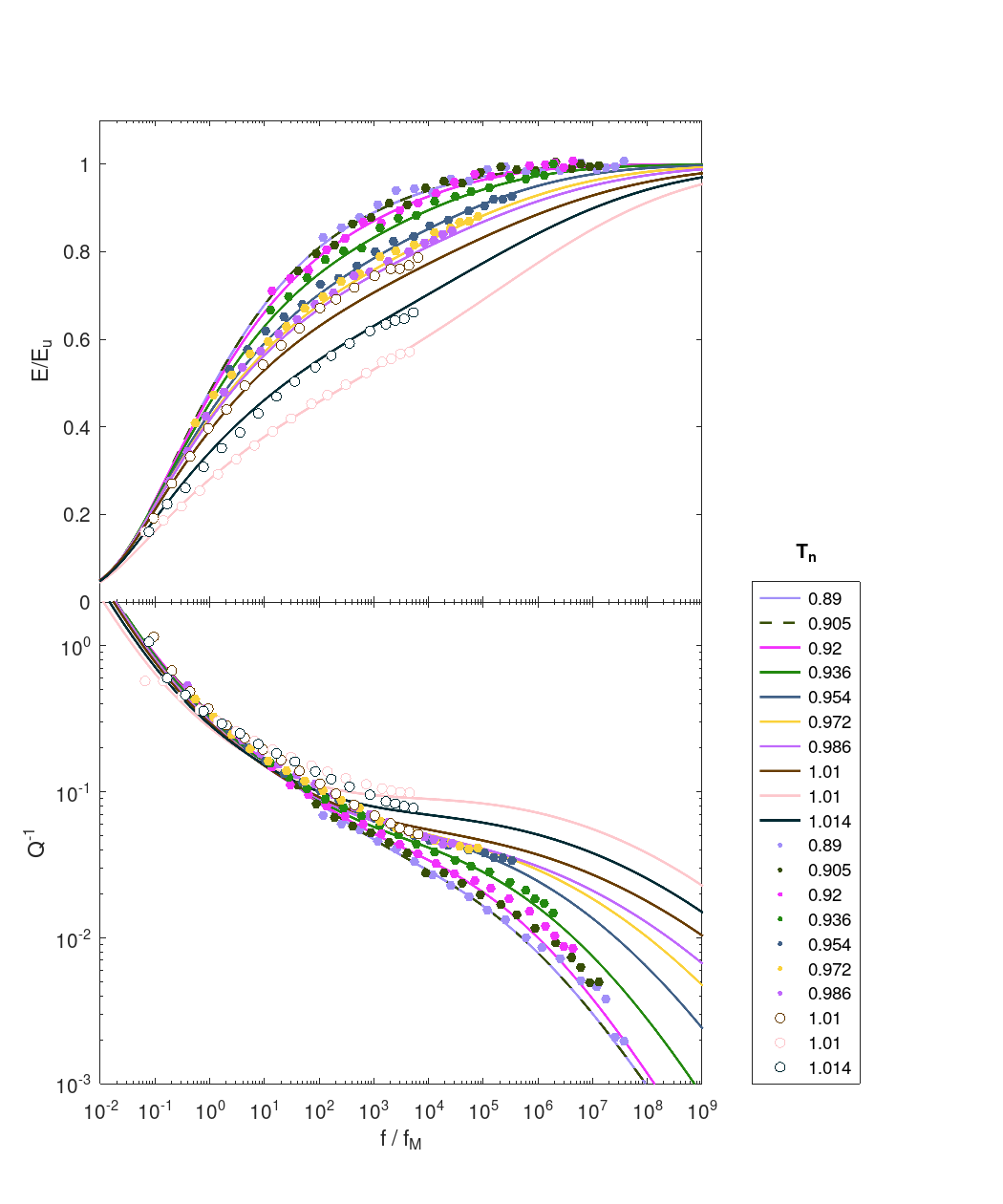
The Project script, Projects/1_LabData/1_Attenuation/FitData_YT24.m reproduces figure 7 from Yamauchi and Takei (2024).